Voice-Activated Systems
Voice-activated systems have rapidly transformed the way we interact with technology, making devices and software more intuitive and accessible. By recognizing and processing spoken language, these systems empower users to execute commands, search for information, and control devices without physical input. The technology lies at the intersection of advanced speech recognition algorithms, machine learning, and natural language processing, opening new horizons in convenience and efficiency for homes, businesses, and personal devices worldwide.
Evolution of Voice-Activated Technology
Early Developments in Voice Recognition
The early days of voice recognition were marked by systems capable of understanding only a limited set of pre-programmed words spoken in controlled environments. Early voice-activated systems relied heavily on isolated word recognition, requiring users to pause between each word for accurate interpretation. Progress was slow due to limited computational power and the complexity of understanding natural language. Despite these challenges, these pioneering systems laid the foundation for contemporary voice recognition by demonstrating the feasibility of allowing machines to interpret spoken input, which inspired further research and innovation.
Breakthroughs in Natural Language Processing
The last decade has seen remarkable strides in natural language processing, significantly enhancing voice-activated systems’ ability to grasp conversational speech and context. Machine learning models, particularly deep neural networks, have dramatically improved accuracy by learning from vast datasets and adapting to diverse linguistic patterns. These breakthroughs allow voice assistants to distinguish between subtle nuances, understand commands embedded in casual conversation, and even respond to follow-up questions. As a result, voice-activated systems today can offer a more fluid, human-like interaction, making them indispensable in homes and workplaces alike.
Integration into Everyday Devices
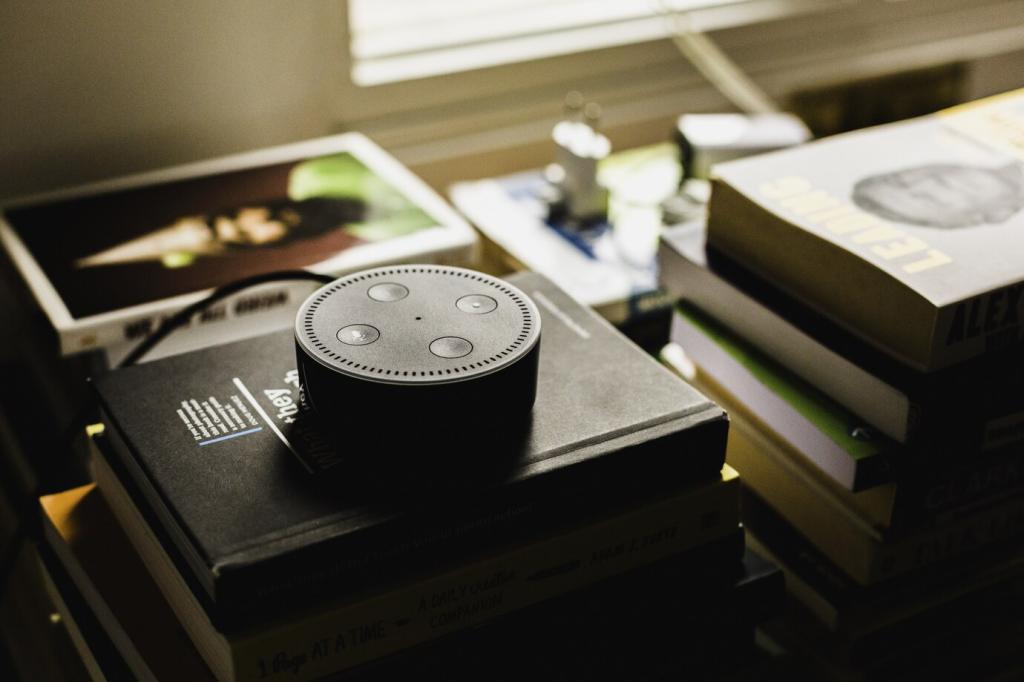
Integrating voice-activated technology into everyday devices has normalized hands-free operation and transformed user experiences. Smartphones, smart speakers, wearables, and automotive systems now routinely feature robust voice control, enabling users to interact with technology safely and conveniently across various environments. This seamless integration means that controlling smart home devices, sending messages, or asking for directions is as simple as speaking a command, reducing barriers to technology adoption and accessibility for people of all ages and abilities.
Previous
Next
Applications and Use Cases
In the realm of smart homes, voice-activated systems have revolutionized how we interact with household devices. Personal assistants such as Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple’s Siri allow users to control lighting, thermostats, security systems, and entertainment devices using simple voice commands. This approach not only adds convenience but also improves accessibility for individuals with mobility or vision challenges. The ability to set reminders, play music, or access information hands-free creates a more seamless and integrated living environment, reflecting the potential for continued innovation in this space.
Challenges and Limitations
Privacy and Data Security Concerns
With voice-activated systems constantly listening for wake words or commands, user privacy and data security remain at the forefront of public concern. Sensitive information could potentially be intercepted or misused if adequate safeguards are not in place. Companies developing these technologies must prioritize encryption, anonymization, and transparent data usage policies to build trust with users. Furthermore, clear opt-in consent processes and the ability for users to review or delete their voice interaction history help reinforce a sense of control over personal data when using these systems.